A straightforward concept, benchmarking nevertheless remains a great way to reveal your organization’s strengths and weaknesses relative to other companies.
A common term within the corporate environment, ‘benchmarking’ is, simply put, measuring one’s own performance against that of others.
In a business context, benchmarking informs organizations on differences between them and their competitors, illustrates strengths and weaknesses, and enables them to make improvements or adapt specific best practices.
Benchmarking may be a one-off event, but can also be treated as a continuous process in which businesses continually seek to improve their operations.
What is ESG benchmarking?
ESG benchmarking is all the above practices applied within an ESG context.
Organizations conducting ESG benchmarking take stock of their various practices within the fields of the environment, their social actions, and their governance policies and strategies, and compare them with those of other companies.
These are usually competitors within the same or similar industries, but could also potentially be other companies of a similar size, those located within the same geographic region, those operating within a similar socio-polical environment, those with similar ESG ratings or scores, or any other number of distinguishing characteristics.
Why is ESG benchmarking important for companies?
ESG benchmarking is important to gauge how a company measures up against its peers in terms of its ESG rating and/or the various ESG-related practices that it employs.
With ESG matters such as green business practices, diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI), corruption, and compensation inequality now firmly in the spotlight, organizations need to be conscious of how they fare in these sorts of areas.
One reason for this is that brand equity is a precious asset which must be protected. Good brand equity enables customers to continue to trust the brand and the values for which it stands, and may even equate to a competitive advantage where customers may choose a brand over others, as well as be willing to pay a price premium.
Not only has the public become more demanding when it comes to business sustainability, but with the advent of the internet and digitally connected social networks, consumers now have access to information like never before.
A company’s lack of transparency on ESG matters now stands a greater chance of being discovered, and furthermore, any customer displeasure regarding negative incidents can spread like wildfire across the internet and social media, harming brand equity and damaging business reputation.
By engaging in ESG benchmarking, companies can keep tabs on their peers and competitors to ensure that they do not fall behind in terms of their ESG-related activities, and potentially suffer reputational damage in comparison to them.
Another important reason to conduct ESG benchmarking is that stakeholders and holding companies are often interested to gauge how their investments are doing in comparison with others.
Investors are cognizant of how ESG scrutiny can give context to a company’s performance, and its potential future success trajectory. Risks that may not previously show up in traditional business analysis may be identifiable via ESG audits, which provide a broader view of an organization’s situation than a pure focus on financial disclosures.
This enables more informed decision-making and the ability to plan more encompassing future business strategies. If ESG performance is indeed linked to business sustainability and long-term success, it makes sense for investors and stakeholders to want to keep an eye on competitors and compare how their investments measure up.
How is ESG benchmarking conducted?
There are multiple ways in which ESG benchmarking can be conducted. A company may wish to compare only one aspect of its ESG to other companies, perhaps because it feels that this may be an area in which it’s lagging (or leading).
Alternatively, it may want a comprehensive analysis of its entire portfolio of ESG activities to compare its strengths and weaknesses with others, and identify areas for improvement.
Although benchmarking can be done subjectively, by analyzing other organizations’ ESG reports and media coverage, most organizations will want a more objective process for measuring how they compare with others. This involves using ESG ratings and scores, which provide a level of standardization and a frame of reference missing from purely subjective assessments.
Conducting a thorough assessment of an organization’s ESG performance can be a sizeable and complex task however, and it’s for this reason that companies may turn to organizations that specialize in ESG benchmarking.
Which organizations provide ESG benchmarks and ratings?
There are multiple large and well-established ESG ratings providers that companies consistently turn to when seeking to obtain both their own ESG scores as well as those of other businesses.
These include MSCI, Sustainalytics, Bloomberg, Moody’s, S&P, CDP, and others.
How are ESG ratings calculated?
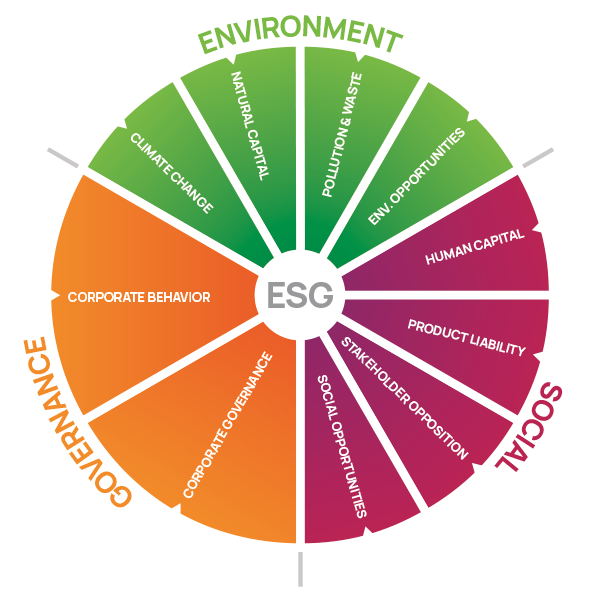
The organizations listed above will generally have key issue frameworks that measure risk and ESG performance across the Environmental, Social, and Governance categories.
MSCI’s key issues, for example, fall under the categories of Climate change, Natural capital, Pollution and waste, and Environmental opportunities (for Environmental issues); Human capital, Product liability, Stakeholder opposition, and Social opportunities (for Social issues); and Corporate governance and Corporate behavior (for Governance issues).
Companies are scored on each issue and MSCI weights them according to their timeframe and potential impact; a shorter timeframe where an issue could have an impact gets weighted more than an issue which may only come into play over the long-term. Issue scores and weights are then combined to derive a rating for the company.
How do I start with ESG benchmarking?
Depending on the size and complexity of the company under evaluation, ESG benchmarking may not be an entirely straightforward process. It is also important to standardize the ESG data being measured as far as possible, so that the benchmarking exercise is meaningful and that accurate comparisons can be made.
For these reasons it’s recommended that companies contact reputable organizations that specialize in this activity, such as the ones listed above.
Alternatively, a good ESG consultancy will be able to advise you on how to get started with your benchmarking process, undertake some of the necessary data collection, formatting, and preparation work, and perhaps even partially or fully conduct the benchmarking procedure itself depending on where its expertise may lie, and how much experience it has in this regard.
No matter which method you use, benchmarking your ESG practices and/or scores against other organizations can be a helpful exercise in figuring out where your strengths and weaknesses lie, and where improvement may be needed.
IsoMetrix’s ESG software can assist in your benchmarking process. By enabling you to collect and manage all your ESG data in a single unified system, you have all the required ESG information easily available to conduct your benchmarking activities. Furthermore, intuitive dashboards enable you to easily visualize your ESG information and access real-time key metrics at-a-glance.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
What are the 3 components of ESG benchmarking?
- Environmental – Focuses on the different impacts a company can have on the environment such as GHG emissions, energy and water usage, dealing with waste, etc.
- Social – Focuses on the company’s relationship with its employees, customers, partners, and the public
- Governance – Focuses on compliance, ethical and legal standards, and transparency within the company
What is sustainability benchmarking?
Much the same as ESG benchmarking, it consists of evaluating how sustainable a company’s operations are across a range of criteria to identify areas of improvement, track progress, and gain insights into how well its managing its environmental and social impacts.
Who can ESG benchmarking be performed by?
ESG benchmarking is usually performed by ESG consultants and specialist ESG rating agencies, but can also be conducted internally by companies themselves.
How is ESG benchmarking conducted?
ESG benchmarking involves collecting relevant company data, and then evaluating performance against internal targets and/or external ESG indices or frameworks.
How can companies improve their ESG benchmarking scores?
Companies can raise their ESG performance via setting ambitious goals, improving reporting accuracy, adopting sustainable practices, and demonstrating governance transparency.

